Learn English
Unlock Your English Listening Potential Using the Power of Silent Films

Silent films offer a unique approach to enhance English listening abilities. By focusing on visual cues and context, learners can develop stronger comprehension skills even without dialogue. This method helps train the ear and brain to process sounds and understand meaning in English more effectively. Utilizing silent movies provides an engaging way to boost your overall English language learning journey.
Table of Contents
- Section 1: Introduction: The Unexpected Power of Silent Films for English Listening
- Section 2: Why Silent Films Work: Focusing on Context and Non-Verbal Cues
- Section 3: Choosing Your Silent Films: Finding Engaging Content
- Section 4: Putting It into Practice: Active Watching Strategies
- Section 5: Beyond the Screen: Activities to Reinforce Learning
- Section 6: Measuring Your Progress and Staying Motivated
- Section 7: Conclusion: Unlock a New Dimension of English Listening
Section 1: Introduction: The Unexpected Power of Silent Films for English Listening
Welcome to an exploration of an unusual method for improving your English listening skills. It might seem counterintuitive: how can films with no talking help you listen better? The answer lies in shifting your focus. Silent films remove the crutch of spoken dialogue, compelling you to pay close attention to everything else – the actors’ expressions, their actions, the setting, and the unfolding plot. By actively interpreting these visual cues, you train your brain to understand context and infer meaning without relying solely on words. This process builds essential comprehension skills that are directly transferable to understanding spoken English, making silent films a surprisingly powerful tool in your language learning journey.
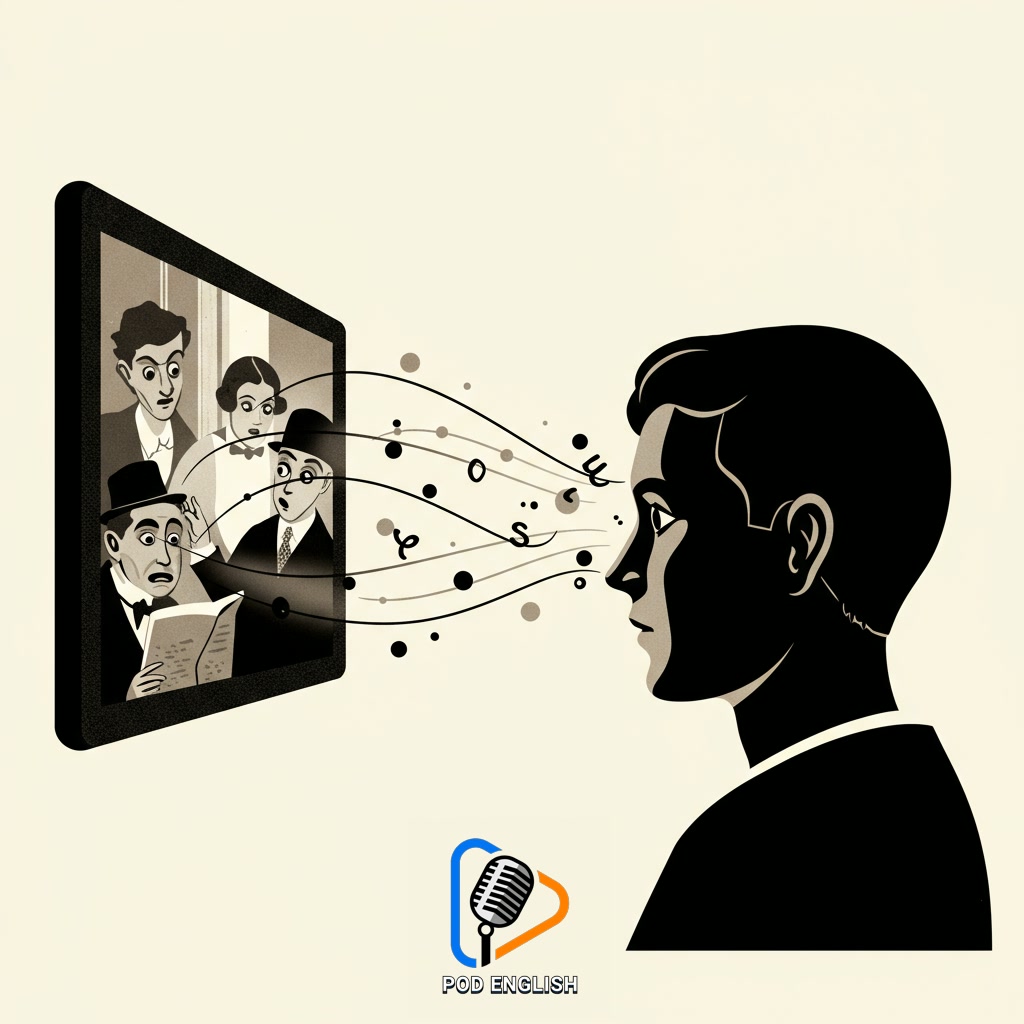

Introduction: The Unexpected Power of Silent Films for English Listening
Section 2: Why Silent Films Work: Focusing on Context and Non-Verbal Cues
Building on the previous point, the answer lies in shifting your focus. Without spoken words, your brain is compelled to rely entirely on visual information. This includes facial expressions, body language, actions, and the setting of the scene. These non-verbal cues provide crucial context, helping you understand the characters’ emotions, intentions, and the overall narrative. By actively interpreting these visuals, you train your brain to connect observable details with meaning, a skill directly applicable to improving listening comprehension in spoken English. When you encounter difficult vocabulary or fast speech, your ability to use context and infer meaning from the situation is greatly enhanced. Silent films sharpen this essential skill in a unique and engaging way.

Why Silent Films Work: Focusing on Context and Non-Verbal Cues
Section 3: Choosing Your Silent Films: Finding Engaging Content
Building on the previous point, the answer lies in shifting your focus. Without spoken words, your brain is compelled to rely entirely on visual information. This includes facial expressions, body language, and the overall scene composition. Now, let’s consider how to choose the right silent films for this practice. Not all silent films are equally effective. Look for movies known for their clear visual storytelling, expressive actors, and relatively easy-to-follow plots. Classic comedies, with their reliance on physical humor and exaggeration, are often excellent starting points. Dramas with strong emotional performances can also be very useful. Consider films with familiar cultural contexts or themes that genuinely interest you, as this will help maintain your focus and engagement. Reading brief descriptions or reviews that comment on the film’s visual clarity can also guide your selection.

Choosing Your Silent Films: Finding Engaging Content
Section 4: Putting It into Practice: Active Watching Strategies
Building on the previous point, the answer lies in shifting your focus. Without spoken words, your brain is compelled to rely entirely on visual information. This includes facial expressions, body language, and the overall setting. To actively put this into practice, dedicate your attention to observing these visual cues intensely. Try to predict what is happening or what a character might be feeling based solely on their actions and expressions. Consider the environment and objects shown, as they often provide crucial context. You can even try to mentally narrate the scene in simple English as you watch. Rewatching certain scenes allows you to catch details you might have missed initially. This active engagement trains your brain to connect visual input with potential meaning, a fundamental skill for better English comprehension when sound is introduced later.

Putting It into Practice: Active Watching Strategies
Section 5: Beyond the Screen: Activities to Reinforce Learning
Building on the previous point, the answer lies in shifting your focus. Without spoken words, your brain is compelled to rely entirely on visual information. This includes facial expressions, body language, and setting details. However, the learning doesn’t stop when the credits roll. To truly reinforce your English listening skills, engage in post-viewing activities. Try describing a scene you just watched, focusing on using descriptive English vocabulary to explain the actions and emotions depicted. Summarize the plot out loud or in writing, forcing yourself to structure your thoughts in English. Discuss the film with a language partner or tutor, explaining character motivations or predicting what dialogue might have been used. These steps move beyond passive viewing, actively training your brain to connect visual understanding with English expression and comprehension, ultimately strengthening your ability to process spoken English when you encounter it.

Beyond the Screen: Activities to Reinforce Learning
Section 6: Measuring Your Progress and Staying Motivated
Measuring your progress with silent films requires a different approach than traditional listening tests. Instead of focusing on specific words or phrases heard, you gauge your improvement by how well you can follow the narrative, understand the characters’ emotions, and anticipate actions purely from visual cues like expressions, body language, and scene composition. Try watching a short film and then writing a brief summary of the plot and key events. Revisit the same film later or watch a different one and compare your level of comprehension. Noticing that you understand more complex visual storytelling or subtle emotional shifts is a clear sign of progress. Staying motivated comes from acknowledging these small victories and setting achievable goals, such as understanding the main plot of one short film per week. The engaging nature of the films themselves can also be a powerful motivator, making the learning process enjoyable.
Measuring Your Progress and Staying Motivated
Section 7: Conclusion: Unlock a New Dimension of English Listening
In conclusion, incorporating silent films into your English learning routine offers a truly unique pathway to enhancing listening comprehension. While traditional methods focus heavily on auditory input alone, the silent film approach trains your brain to synthesize meaning from a broader range of cues, including body language, facial expressions, and situational context, as highlighted when measuring progress. This method doesn’t replace standard listening practice but complements it, adding a powerful new dimension to how you process and understand spoken English, even when the sound is present. By learning to ‘listen’ with your eyes, you become a more versatile and effective communicator, unlocking a deeper level of understanding and truly maximizing your English listening potential.

Conclusion: Unlock a New Dimension of English Listening













