Learn English
Learn Professional English Email Writing for Work
This content focuses on mastering professional English email communication essential for the workplace. It covers key principles and techniques for crafting clear, concise, and effective messages. Individuals will gain practical skills to enhance their written communication, contributing to their broader journey of learning English for career advancement. Mastering these techniques is a vital step in developing strong professional English proficiency.
Table of Contents
- Section 1: Why Professional English Email Writing Matters at Work
- Section 2: Understanding the Anatomy of a Professional Email
- Section 3: Crafting Clear, Concise, and Effective Messages
- Section 4: Mastering Tone and Politeness in Business Communication
- Section 5: Writing Different Types of Work Emails: Examples and Best Practices
- Section 6: Proofreading and Avoiding Common Mistakes
Section 1: Why Professional English Email Writing Matters at Work
Professional English email writing is crucial in today’s workplace because emails serve as the main channel for formal communication. Mastering this skill ensures your messages are clear, concise, and easily understood by colleagues, clients, and superiors, regardless of their English proficiency levels. Effective emails prevent misunderstandings, build credibility, and project a professional image. They facilitate smooth collaboration, aid in documenting important information, and contribute directly to efficiency and productivity. For anyone learning English for career advancement, developing strong email writing abilities is a fundamental step. It demonstrates your commitment to professional standards and significantly enhances your ability to navigate the global business environment, making it an essential component of your overall English learning journey for work.

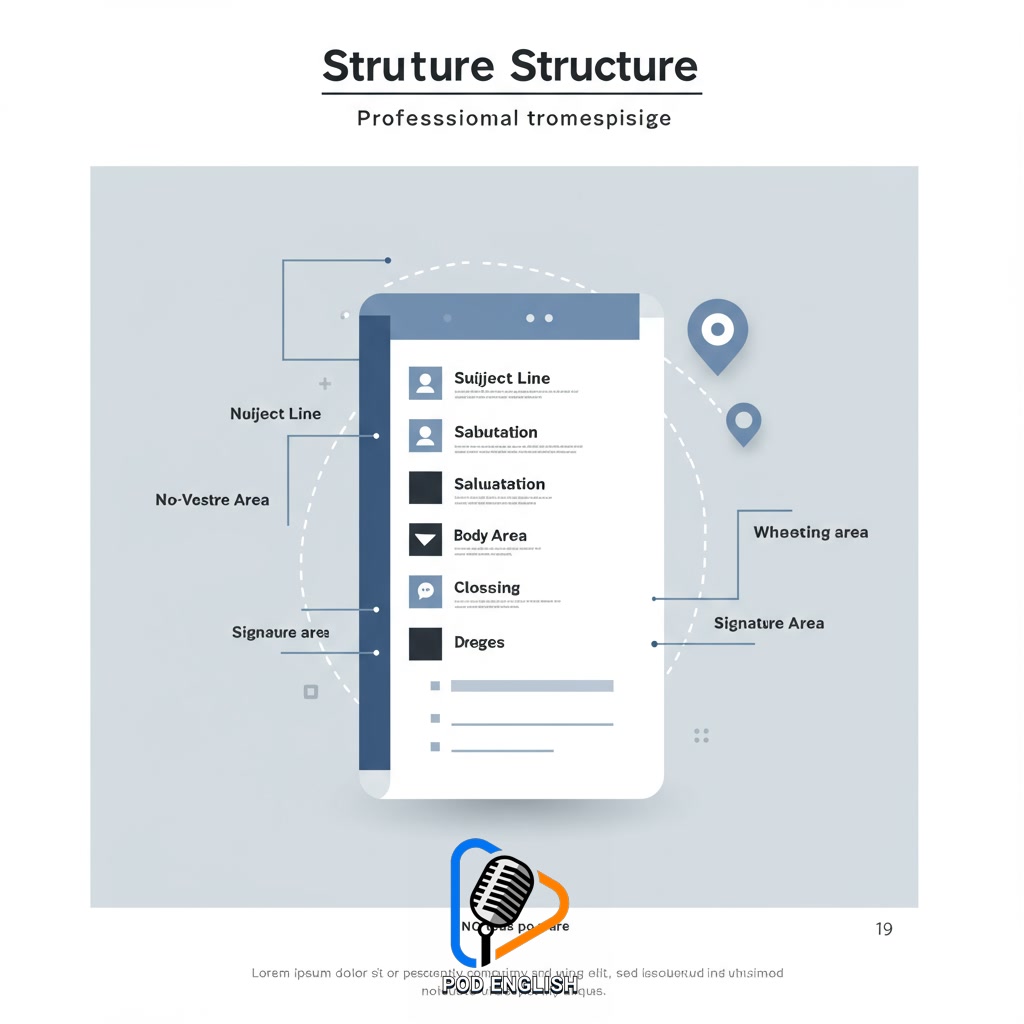
Section 2: Understanding the Anatomy of a Professional Email
To master professional English email writing, it’s essential to understand its fundamental structure, often referred to as the ‘anatomy.’ A typical professional email consists of several key components working together to convey your message effectively. This includes a clear and concise Subject Line, which immediately tells the recipient the email’s purpose; a proper Salutation, setting a professional tone; the Body, where you present your main points clearly and logically; a polite Closing phrase; and your Signature, providing necessary contact information. Learning to structure your thoughts within this framework is a vital step in developing strong written communication skills as part of your English learning journey for career advancement.
Section 3: Crafting Clear, Concise, and Effective Messages
Beyond understanding the basic structure, mastering professional English email writing requires focusing on the message itself: making it clear, concise, and effective. Clarity means your reader can easily understand your meaning without confusion. Achieve this by using simple vocabulary, shorter sentences, and avoiding jargon or ambiguity. Conciseness is about getting straight to the point and including only necessary information, saving the reader time and effort. Be direct and remove redundant words or phrases. Effectiveness ensures your email achieves its intended purpose, whether it’s to inform, request, or persuade. By prioritizing these three qualities, you enhance your communication skills, making your emails more professional and contributing significantly to your overall English proficiency for career growth.

Section 4: Mastering Tone and Politeness in Business Communication
Building upon clarity and conciseness, mastering professional English email also requires careful attention to tone and politeness. Your tone is the attitude conveyed through your writing, influencing how your message is received. In business, maintaining a polite and respectful tone is crucial for fostering positive relationships, avoiding misunderstandings, and upholding your professional image. This involves choosing appropriate vocabulary (e.g., using ‘please’ and ‘thank you’), structuring sentences politely, and selecting suitable greetings and closings. Being mindful of cultural nuances in politeness can further enhance your communication effectiveness. A polite tone ensures your message is not only understood but also appreciated, making interactions smoother and more productive in the workplace.

Section 5: Writing Different Types of Work Emails: Examples and Best Practices
Building upon the foundation of clarity, conciseness, tone, and politeness, this section delves into the practical application of these principles across various common types of work emails. Not all professional messages are written the same way; effective communication requires adapting your approach based on your purpose. We will explore examples and best practices for emails like making inquiries, sending requests, providing updates, confirming details, and writing formal announcements. Understanding the specific structure, appropriate tone, and key phrases for each type is vital for crafting impactful messages in English. By studying these examples, you will gain practical insights into tailoring your writing for different workplace scenarios, further enhancing your professional English skills.

Section 6: Proofreading and Avoiding Common Mistakes
After carefully crafting your email for clarity, conciseness, appropriate tone, and politeness, the crucial final step is meticulous proofreading. Skipping this stage can undermine your message and professional image. Common mistakes include grammatical errors, spelling typos, incorrect punctuation, and unclear phrasing. Taking the time to review your email thoroughly helps catch these issues before they are sent. Strategies like reading your email aloud, using spell check and grammar tools, and even taking a short break before reviewing can significantly improve accuracy. Ensuring your email is free of errors demonstrates attention to detail and respect for the recipient, reinforcing your credibility in professional communication.














