Learn English
Sharpen Your Mind: Hydration for Better English Learning

This content highlights the crucial link between proper hydration and enhanced cognitive function. It explains how maintaining adequate fluid intake can significantly improve mental clarity, focus, and memory. These cognitive benefits are particularly advantageous for individuals actively engaged in learning English, as optimal brain performance supports better comprehension and retention of new information. Therefore, prioritizing hydration is presented as a simple yet effective method to sharpen the mind and optimize the English learning experience.
Table of Contents
- Section 1: The Vital Link: Why Hydration Matters for Your Brain
- Section 2: Dehydration’s Silent Sabotage: How Low Water Intake Affects Cognitive Function
- Section 3: Sharpening Your Focus: Hydration and Concentration for English Learning
- Section 4: Memory Boost: How Staying Hydrated Aids Language Retention
- Section 5: Practical Tips: Simple Ways to Stay Hydrated Throughout Your Learning Day
- Section 6: Beyond Thirst: Recognizing Dehydration Signs and Taking Action
- Section 7: Unlock Your Potential: Making Hydration a Key Part of Your English Learning Strategy
Section 1: The Vital Link: Why Hydration Matters for Your Brain
Your brain, like every other part of your body, relies heavily on water to function correctly. Water is essential for transporting oxygen and nutrients to brain cells and removing waste products. Maintaining proper hydration ensures efficient blood flow to your brain, which is crucial for optimal cognitive performance. When your brain is well-hydrated, you experience better mental clarity, improved focus, and enhanced concentration. Even mild dehydration can impair these vital functions, making it more challenging to pay attention, process new information, and retain what you learn. Understanding this vital link highlights why keeping yourself adequately hydrated is a simple yet powerful strategy to support your brain’s health and readiness for learning.
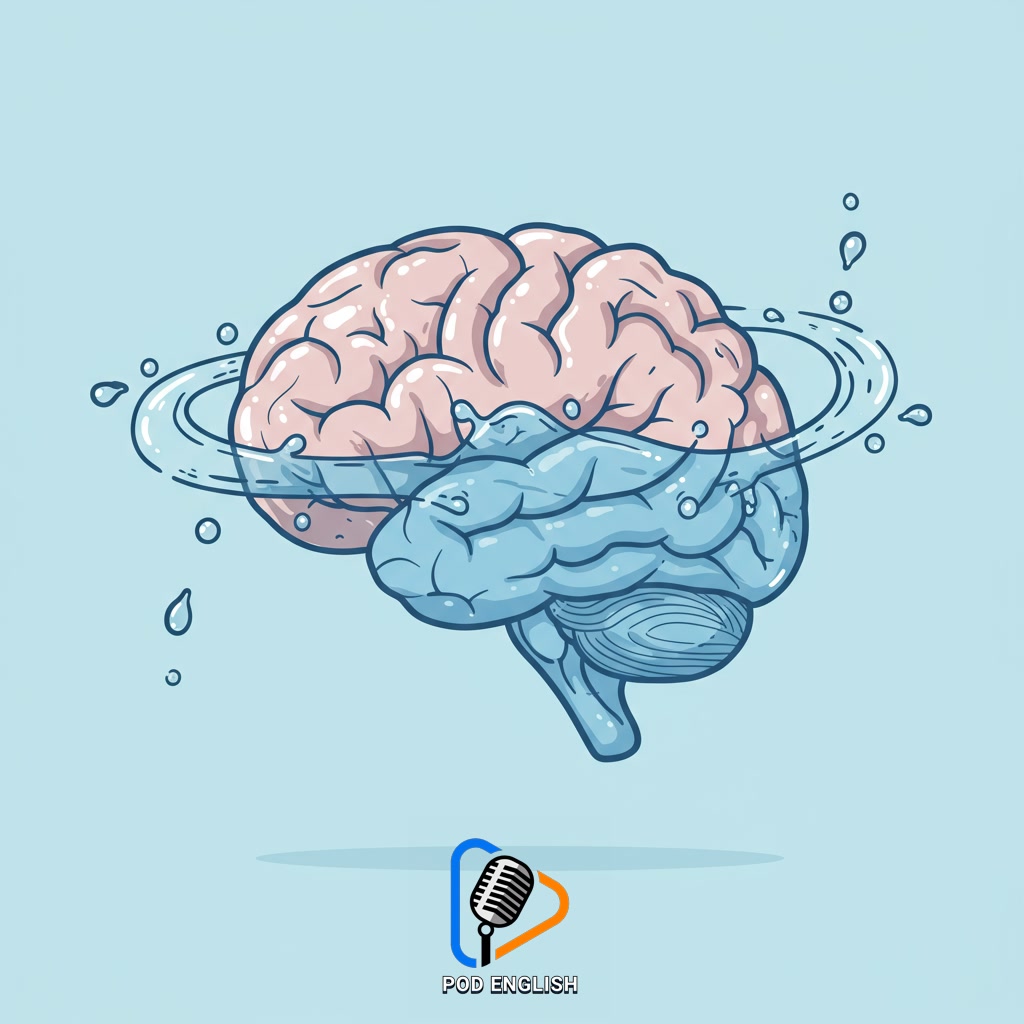

The Vital Link: Why Hydration Matters for Your Brain
Section 2: Dehydration’s Silent Sabotage: How Low Water Intake Affects Cognitive Function
When your body doesn’t receive enough water, a state known as dehydration occurs. This lack of hydration significantly impacts your brain’s performance. Blood flow to the brain can decrease, reducing the efficient delivery of vital oxygen and nutrients necessary for thinking and processing information. Waste products also become harder to remove effectively. As a result, even mild dehydration can lead to noticeable cognitive impairments. You might experience fatigue, difficulty concentrating, struggle to focus on tasks, find it harder to recall information, and feel mentally sluggish. This ‘silent sabotage’ directly hinders your ability to learn and retain new English vocabulary and grammar.
Dehydration’s Silent Sabotage: How Low Water Intake Affects Cognitive Function
Section 3: Sharpening Your Focus: Hydration and Concentration for English Learning
Following the reduced cognitive function caused by dehydration, maintaining adequate hydration levels is crucial for optimizing brain performance, especially when engaged in demanding tasks like learning English. Proper hydration ensures sufficient blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain, directly impacting your ability to concentrate and sustain focus. When you are well-hydrated, your mind is sharper, allowing you to absorb new vocabulary and grammar rules more effectively, pay attention during lessons or study sessions, and maintain the concentration needed for reading comprehension or listening practice. This enhanced focus makes the learning process more efficient and less tiring, ultimately helping you make faster progress in your English studies.

Sharpening Your Focus: Hydration and Concentration for English Learning
Section 4: Memory Boost: How Staying Hydrated Aids Language Retention
Building on optimizing brain performance, adequate hydration plays a vital role in enhancing memory function, a critical aspect of mastering English. When your brain is properly hydrated, neural communication pathways become more efficient. This improved efficiency directly supports the processes of encoding new information – like vocabulary or grammatical structures – into long-term memory and subsequently retrieving it when needed. Dehydration, even mild, can impair these processes, making it harder to retain what you’ve learned and recall it during conversation or practice. Therefore, consistently staying hydrated acts as a simple yet powerful tool to strengthen memory consolidation and recall, significantly boosting your ability to remember and utilize new English language elements effectively.

Memory Boost: How Staying Hydrated Aids Language Retention
Section 5: Practical Tips: Simple Ways to Stay Hydrated Throughout Your Learning Day
Building on optimizing brain performance, adequate hydration plays a vital role in enhancing memory function, a critical aspect of mastering English. To ensure you stay properly hydrated throughout your learning day, integrate simple habits. Keep a reusable water bottle filled and within easy reach on your study desk or wherever you practice English. Make it a routine to take sips regularly, perhaps during short breaks between exercises or while reviewing vocabulary. Consider setting reminders on your phone if you tend to forget. Drinking a glass of water before starting a study session can also help prepare your mind. Furthermore, incorporating hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables into your snacks contributes to overall fluid intake. These small, consistent efforts will help maintain optimal cognitive function, supporting clearer thinking and better retention of new English information.

Practical Tips: Simple Ways to Stay Hydrated Throughout Your Learning Day
Section 6: Beyond Thirst: Recognizing Dehydration Signs and Taking Action
Building on optimizing brain performance and memory, it’s crucial to recognize when your body needs more water, even before feeling intense thirst. Thirst is often a late sign of dehydration. Pay attention to subtle indicators like feeling tired, experiencing a mild headache, dizziness, or having a dry mouth. Another key sign is the color of your urine; if it’s dark yellow, you likely need to drink more water. Recognizing these signals early is vital for maintaining cognitive function, which directly impacts your ability to focus and absorb new English vocabulary and grammar. The simple action is to drink water immediately and make a conscious effort to sip water regularly throughout your study sessions and the day.
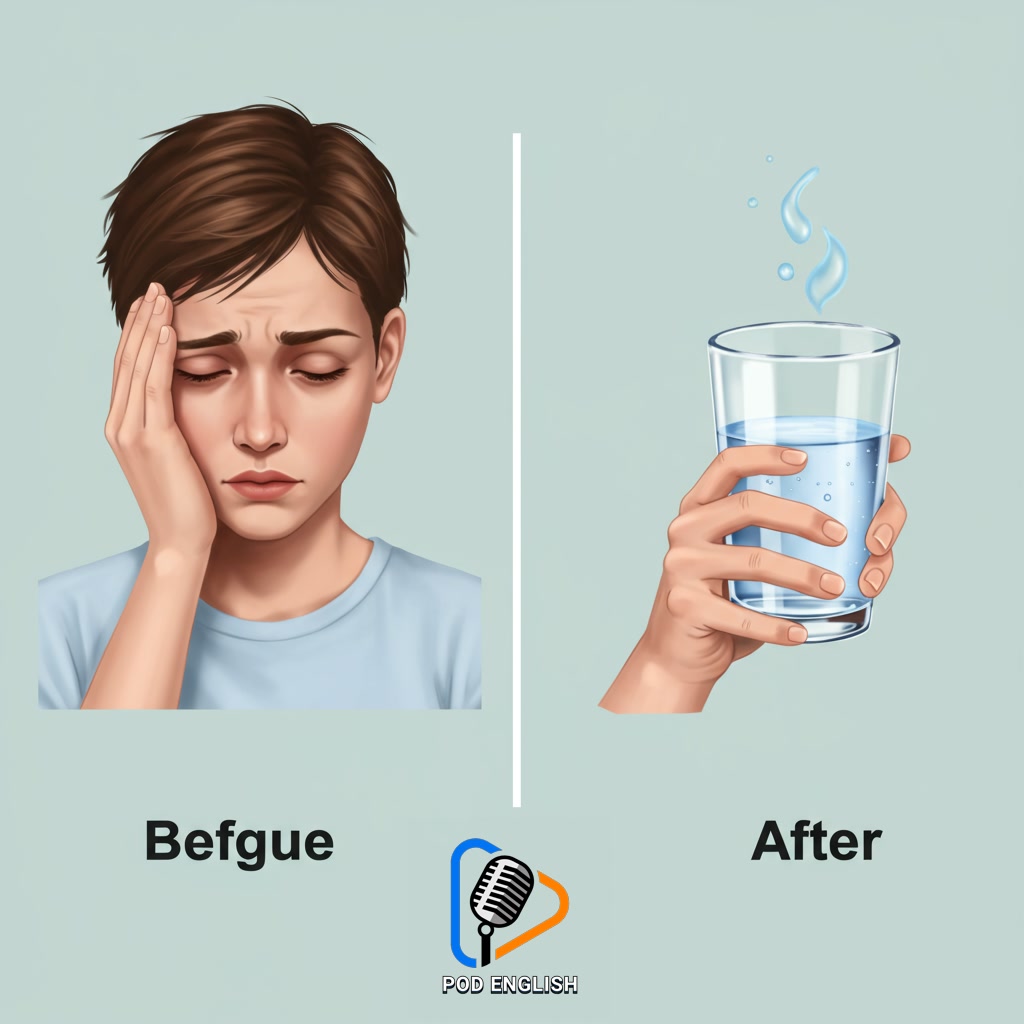

Beyond Thirst: Recognizing Dehydration Signs and Taking Action
Section 7: Unlock Your Potential: Making Hydration a Key Part of Your English Learning Strategy
Building on recognizing early signs, proactively integrating hydration into your English learning routine is key to sustained focus and cognitive efficiency. Don’t wait until you feel thirsty to grab water. Keep a water bottle readily accessible during study sessions, breaks, and even while listening to English podcasts or watching videos. Make a conscious effort to take small sips regularly throughout your learning time. This consistent intake helps maintain optimal brain function, preventing the dip in concentration and mental fatigue that dehydration can cause. By making hydration a non-negotiable part of your study strategy, you create a better environment for your brain to absorb, process, and retain new vocabulary, grammar, and listening skills, truly unlocking your learning potential.

Unlock Your Potential: Making Hydration a Key Part of Your English Learning Strategy













